Basic Thread Terms – Part 2
Additional Terms
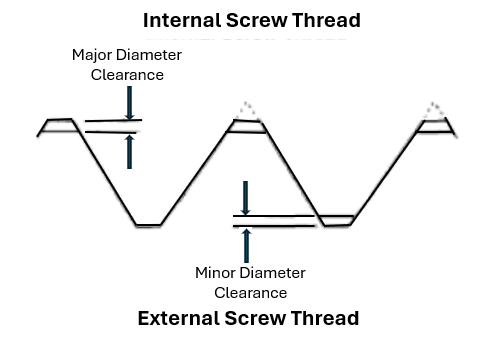
Major Diameter Clearance – The difference between the major diameter (crest) of the external thread and the major diameter (root) of the mating internal thread.
Minor Diameter Clearance – The difference between the minor diameter (crest) of the thread and the minor diameter (root) of the mating external thread.
Length of Engagement – The length that is engaged measured parallel to the axis when mating parts are assembled.
Symmetrical Thread Form – Any thread form having a basic design profile with equal crest and root truncation and equal flank angles. The unified thread form pictured has equal 30° flank angles and equal crest and root truncati
Truncation – The distance measured perpendicular to the axis between the theoretical sharp apex and actual flat at crest (or root). In the Symmetrical Thread form diagram the truncation is designated as “t”.
Unified Screw Thread Designations
UNC – Unified National Coarse series
UNF – Unified National Fine series
UNEF – Unified National Extra Fine series
UN – Unified National Constant Pitch series
UNS – Unified National special Diameter Pitch Combination
UNR – Unified threads having .108P – .144P root radius on external thread
UNJ – Unified threads having closely controlled .150P – .180P root radius on external threads and increased minor diameter on internal threads – used mainly on critical aeronautical applications
UNC – Unified National Coarse series
UNF – Unified National Fine series
UNEF – Unified National Extra Fine series
UN – Unified National Constant Pitch series
UNS – Unified National special Diameter Pitch Combination
UNR – Unified threads having .108P – .144P root radius on external thread
UNJ – Unified threads having closely controlled .150P – .180P root radius on external threads and increased minor diameter on internal threads – used mainly on critical aeronautical applications
Standard UNC and UNF thread sizes are generally preferred if they are suitable for the application. Taps, dies, chasers and other threading tools for them as well as thread gages are widely available from stock at lowest costs. If one or both components involve a commercial fastener (nut, screw or bolt, etc.), again, standard sizes are the most economical.
