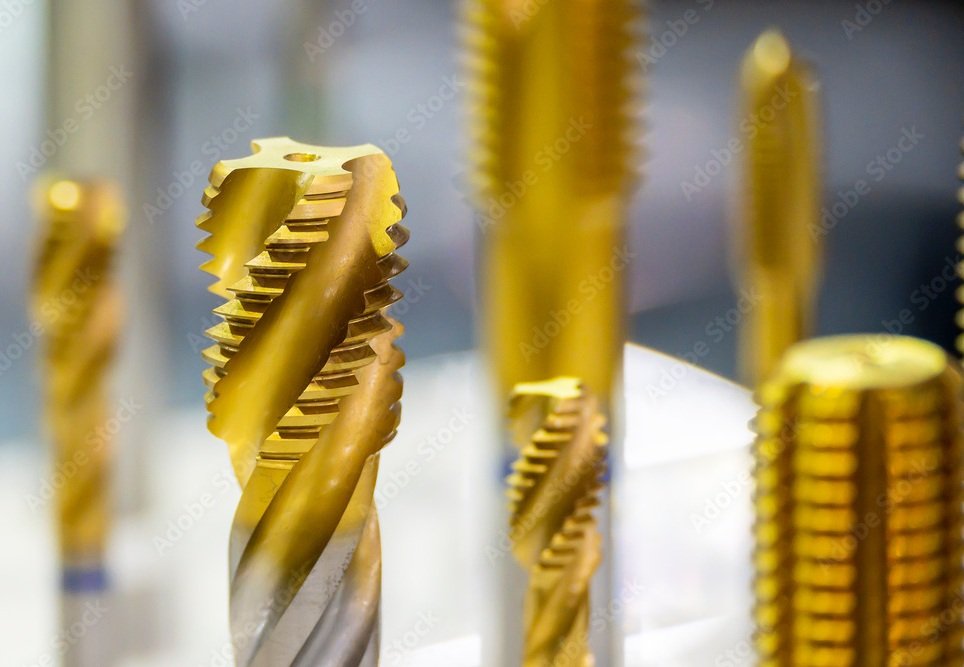
Basic Thread Terms
Major diameter – The largest diameter of a straight thread.
Minor Diameter – The smallest diameter of a straight thread.
Pitch – The distance from a point on a screw thread to a corresponding point on the next thread, measured parallel to the axis. For Imperial threads the formula is as follows:
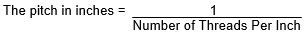
Example: 20 TPI Pitch = 1/20 = .0500
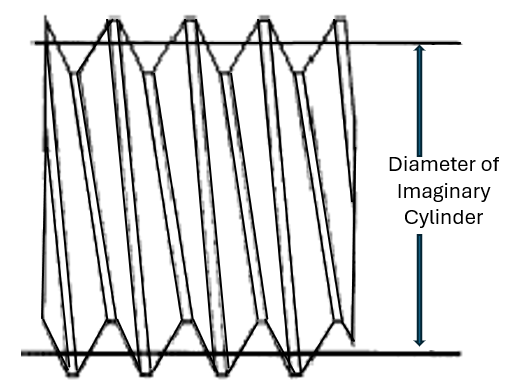
Pitch Diameter – On a straight screw thread, the diameter of an imaginary cylinder, the surface of which would pass through the threads at such points as to make equal the width of the thread ridge and the width of the thread groove.
On a tapered screw thread, the diameters at a point perpendicular to the axis of an imaginary cone. The surface of which would pass through the threads at such points as to make equal the width of the threads and the width of the spaces cut by the surface of the cone. From this definition it is apparent that the pitch diameter of each thread varies from the adjacent thread by a constant ratio.
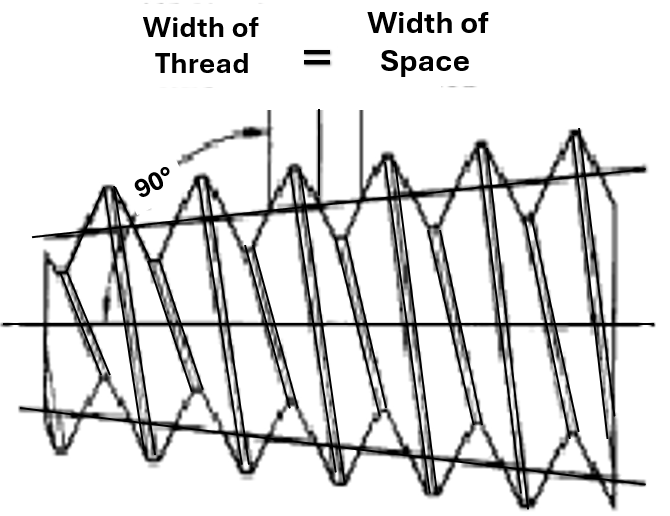
Angle of Thread – The angle included between the flanks of the thread measured in an axial plane.
Half Angle of Thread – The angle included between a flank of the thread and the normal (90°) to the axis, measured in an axial plane.
Lead – The distance a screw thread advances axially in one turn. On a single lead thread the lead and pitch values are identical. On a double lead thread the lead is 2 x pitch; on a triple lead thread the lead is 3 x pitch, etc.
Lead Angle – The angle made by the helix of a thread at the pitch diameter with a line perpendicular to the axis. This is sometimes referred to as the Helix Angle.
Major Diameter Clearance – The difference between the major diameter (crest) of the external thread and the major diameter (root) of the mating internal thread.
Minor Diameter Clearance – The difference between the minor diameter (crest) of the thread and the minor diameter (root) of the mating external thread.
Length of Engagement – The length that is engaged measured parallel to the axis when mating parts are assembled.
Symmetrical Thread Form – Any thread form having a basic design profile with equal crest and root truncation and equal flank angles. The unified thread form pictured has equal 30º flank angles and equal crest and root truncation.
Truncation – The distance measured perpendicular to the axis between the theoretical sharp apex and actual flat at crest (or root). In the Symmetrical Thread form diagram the truncation is designated as “t”.
